Solder paste printing is undeniably one of the most formidable challenges in quality assurance within the realm of electronic manufacturing. This challenge escalates as technological advancements usher in a fusion of large modules and diminutive chip components on densely populated printed circuit boards. Consequently, establishing a robust quality assurance protocol for solder paste printing has evolved into an imperative necessity. This article elucidates a method for safeguarding high-quality data originating from both solder paste printers and inspection machines within the electronic assembly manufacturing domain. This invaluable data serves as a constructive feedback mechanism for refining the solder paste printing process.
Facing Challenges with Solder Paste Printing
The Solder Paste Printing Process Within the sphere of electronic manufacturing, solder paste printing emerges as a pivotal and intricate process. Its primary objective is to consistently apply the precise amount of paste at the correct position, with meticulous precision, each time a print is executed. Although the process might seem relatively straightforward, the quality of the print, in conjunction with the printed circuit board, serves as the bedrock for the entire surface mount process. An impeccable print outcome is the prerequisite for achieving a successful soldering result, while subpar printing can cascade into additional process complications as the product traverses the manufacturing pipeline.
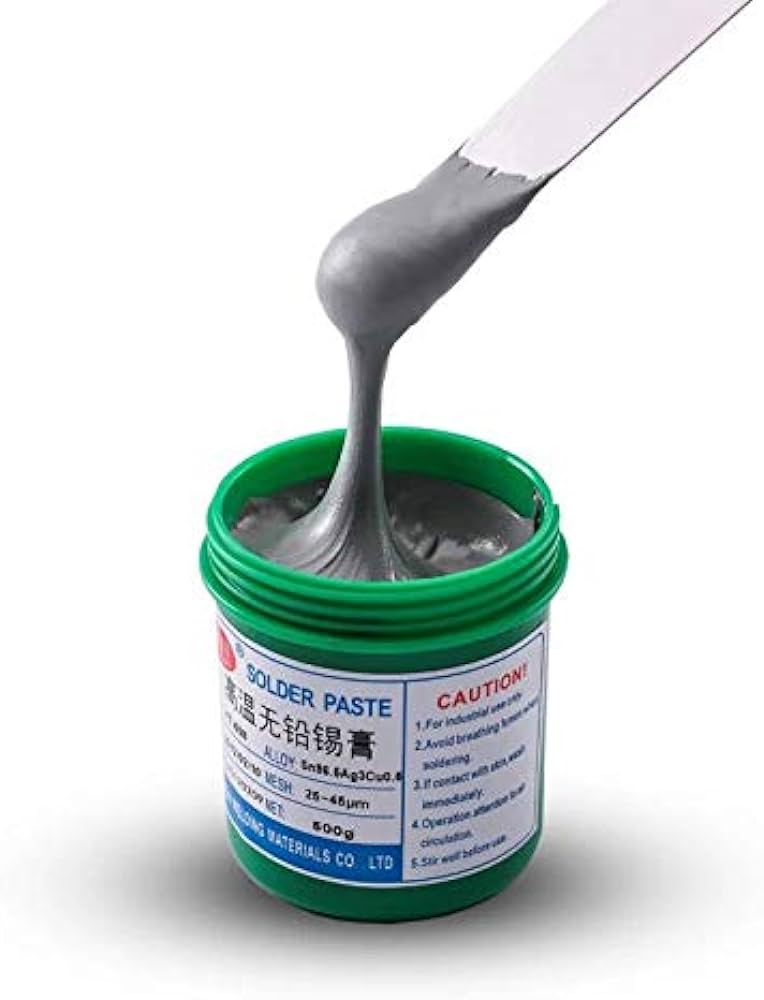

Navigating Challenges in Solder Paste Printing The path to consistent solder paste printing is fraught with challenges, particularly when dealing with less-than-professional PCB assembly companies, often grappling with the demands of large orders and tight deadlines. To ensure a successful outcome, PCB assemblers must adhere to several fundamental principles:
- Meticulously Craft the Stencil: The accuracy of the solder paste printing process hinges on the precision of the stencil. A subpar, imprecise, or inadequately crafted stencil will invariably yield unreliable results.
- Accurate Screen Printer Programming: Solder paste screen printing devices necessitate exact measurements and precise calibration to execute their tasks with unwavering accuracy. Expertise in screen printing programming is a prized skill within the PCB industry.
- Precise Application of Solder Paste: The art lies in applying the right quantity of solder paste. Excessive paste results in imperfect outlines, while insufficient paste prevents the SMDs from adhering.
- Selection of the Appropriate Process: Two primary methods exist for achieving a satisfactory print—mesh screen printing and metal screen printing. While the former represents a cost-effective option, it falls short when dealing with small SMDs that demand precision attachment.
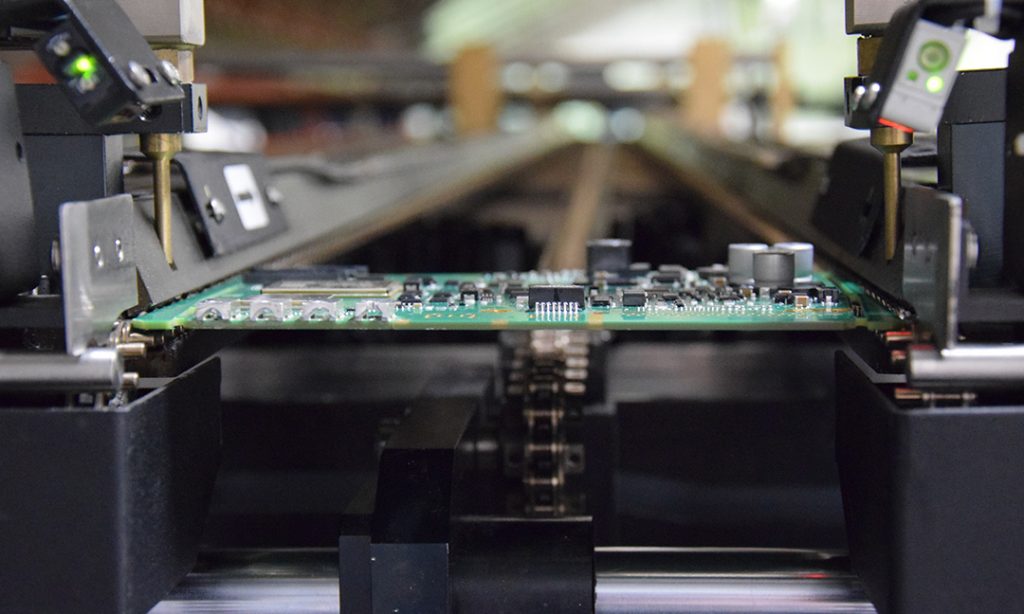
By meticulously attending to the solder paste printing process, you can gauge the true capabilities of a PCB assembly company. Consider this process as the litmus test for professionalism and competence.
Pingback: Ensuring Top-Quality PCBs: Advanced Inspection Methods you must know. - Contract Manufacturing
Pingback: Understanding and Selecting Components for Electron Devices and Circuits in PCB Assembly - Contract Manufacturing